Daily Newsletter February 15, 2012
Today's Topic: Amino Acid Biosynthesis
There are 20 amino acids used in translation, and each one has to be synthesized. One of the hardest components of the amino acid to get is the amino group. Nitrogen is the primary limiting nutrient in terrestrial ecosystems, so organisms either have to fix nitrogen or scavenge for it. (a good example of adaptation to nitrogen can be seen in insectivorous plants: they digest insects to get nitrogen).
Glutamate is one of the critical amino acids when it comes to biosynthesis, because glutamate easily undergoes transamination. In this process, the amino group can be moved to a ketoacid (usually from TCA) to construct other amino acids. So our first step in understanding amino acid biosynthesis is to look at glutamate biosynthesis.
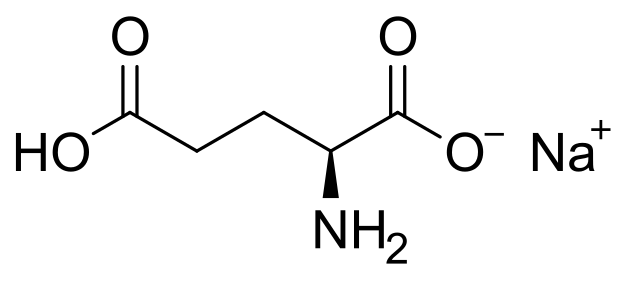 | ||
| Glutamate |
Glutamate can then be used with Transaminase to make other amino acids. Here is an example of glutamate pyruvate transaminase:
Daily Challenge: Using your book and online resources, list all of the amino acids that can be made from glutamate. Which of these are considered essential or non-essential amino acids to humans? (do bacteria have essential and non-essential amino acids?). Articulate at least two amino acid biosynthetic pathways not previously described.
Admin Note: Only one student has completed the calibrations. Do not wait until the last minute. You will only hurt yourself and your reviews if you wait.


No comments:
Post a Comment